Protected Branches
Permissions in GitLab are fundamentally defined around the idea of having read or write permission to the repository and branches. To prevent people from messing with history or pushing code without review, we've created protected branches.
Overview
By default, a protected branch does four simple things:
- it prevents its creation, if not already created, from everybody except users with Master permission
- it prevents pushes from everybody except users with Master permission
- it prevents anyone from force pushing to the branch
- it prevents anyone from deleting the branch
See the Changelog section for changes over time.
Additional functionality for GitLab Enterprise Edition:
- Restrict push and merge access to certain users
Configuring protected branches
To protect a branch, you need to have at least Master permission level. Note
that the master branch is protected by default.
- Navigate to the main page of the project.
-
In the upper right corner, click the settings wheel and select Protected branches.
-
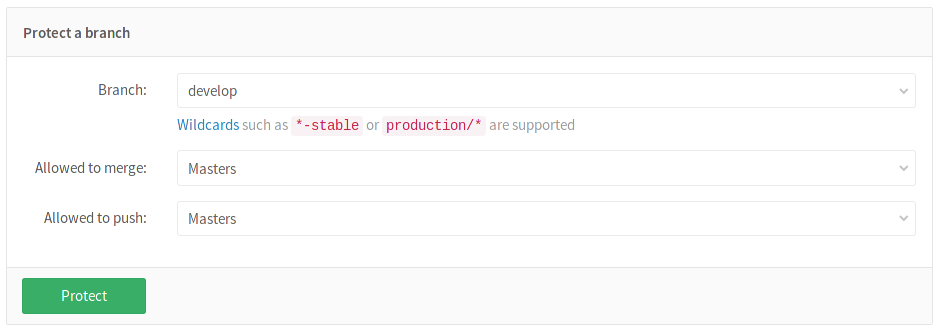
From the Branch dropdown menu, select the branch you want to protect and click Protect. In the screenshot below, we chose the
developbranch. -
Once done, the protected branch will appear in the "Protected branches" list.
Using the Allowed to merge and Allowed to push settings
Introduced in GitLab 8.11.
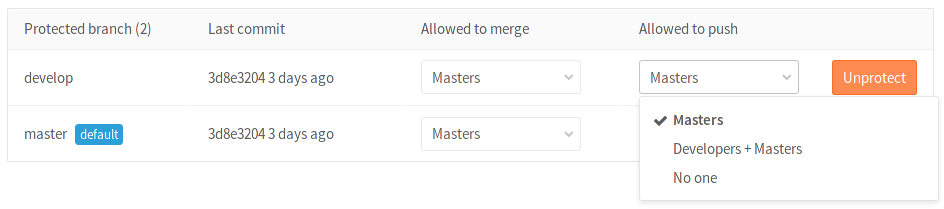
Since GitLab 8.11, we added another layer of branch protection which provides more granular management of protected branches. The "Developers can push" option was replaced by an "Allowed to push" setting which can be set to allow/prohibit Masters and/or Developers to push to a protected branch.
Using the "Allowed to push" and "Allowed to merge" settings, you can control the actions that different roles can perform with the protected branch. For example, you could set "Allowed to push" to "No one", and "Allowed to merge" to "Developers + Masters", to require everyone to submit a merge request for changes going into the protected branch. This is compatible with workflows like the GitLab workflow.
However, there are workflows where that is not needed, and only protecting from force pushes and branch removal is useful. For those workflows, you can allow everyone with write access to push to a protected branch by setting "Allowed to push" to "Developers + Masters".
You can set the "Allowed to push" and "Allowed to merge" options while creating a protected branch or afterwards by selecting the option you want from the dropdown list in the "Already protected" area.
If you don't choose any of those options while creating a protected branch, they are set to "Masters" by default.
Wildcard protected branches
Introduced in GitLab 8.10.
You can specify a wildcard protected branch, which will protect all branches matching the wildcard. For example:
| Wildcard Protected Branch | Matching Branches |
|---|---|
*-stable |
production-stable, staging-stable
|
production/* |
production/app-server, production/load-balancer
|
*gitlab* |
gitlab, gitlab/staging, master/gitlab/production
|
Protected branch settings (like "Developers can push") apply to all matching branches.
Two different wildcards can potentially match the same branch. For example,
*-stable and production-* would both match a production-stable branch.
In that case, if any of these protected branches have a setting like
"Allowed to push", then production-stable will also inherit this setting.
If you click on a protected branch's name, you will be presented with a list of all matching branches:
Changelog
8.11
- Allow creating protected branches that can't be pushed to gitlab-org/gitlab-ce!5081
8.10
- Allow developers to merge into a protected branch without having push access gitlab-org/gitlab-ce!4892
- Allow specifying protected branches using wildcards gitlab-org/gitlab-ce!4665